
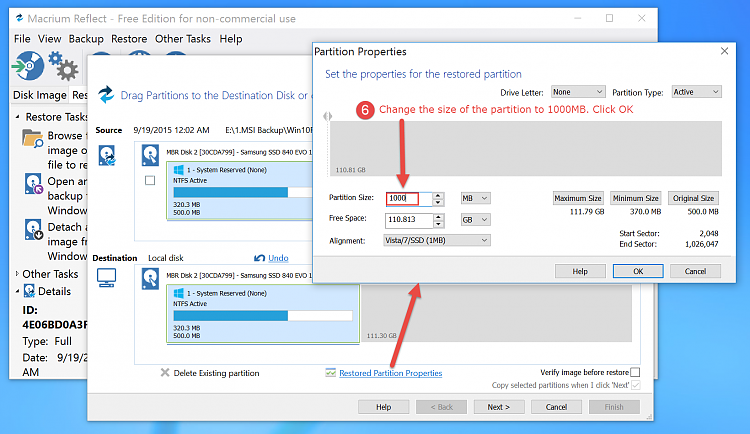
In the System Recovery Options dialog box, click Command Prompt. Select the operating system that you want to repair, and then click Next. Select a language, a time, a currency, a keyboard, or an input method, and then click Next. Bootrec.exe from the Windows 7 install disk as per instructions: Put the Windows Vista or Windows 7 media in the DVD drive, and then start the computer. What is the remedy to 'inform' the boot sector of the new location of the large main partition?Ī. However, moving the large partition to the back with gParted creates a problem because the boot partition was not update to reflect the large partition move: Now that the unallocated partition is adjacent to the target partition, gParted is able to resize the target partition. The empty partition was "moved between" the other two partitions: What UNIX options are available to increase partition size? UPDATES
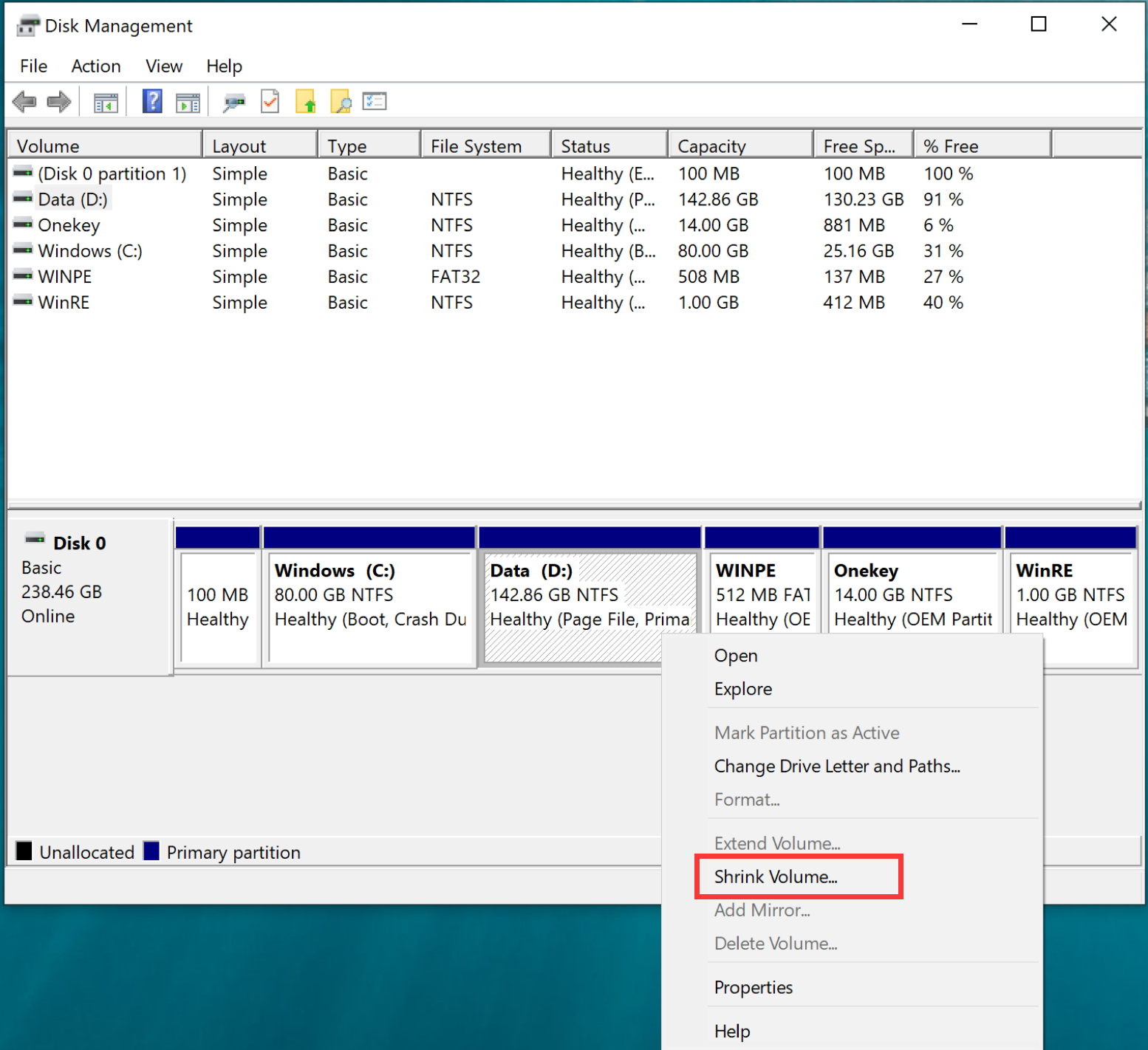
Why is gParted unable to increase the size of said partition? Solution 2: Expand your computers System Reserved partition Solution 3: Perform a System Restore Solution 4: Reinstall Windows 10 Solution 5: Check. I am able engage gParted via sysrecuecd QUESTIONS Attempts to use gParted and diskmgmt.msc to augment partition size were met with greyed-out controls. I was able to reduce the size of the C:\ partition by 500 GB using Window's native diskmgmt.msc tool. Microsoft expects an MSR to be present on every GPT disk, and recommends it to be created as the disk is initially partitioned.The goal is to expand a Windows 7 SSD System Reserved Partition from 39MB and add 500MB to the partition. The MSR should be located after the EFI System Partition (ESP) and any OEM service partitions, but it must be located before any primary partitions of bootable Windows operating systems. This size gets reduced as portions of the MSR are taken to be used, as described above.īeginning in Windows 10, the minimum size of the MSR is 16 MB which the installer allocates by default. The starting size of an MSR depends on disk size and usually aligns with the following table. Such software components can create a small software-component specific partition from a portion of the space reserved in the MSR partition. Microsoft reserves a chunk of disk space using this MSR partition type, to provide an alternative data storage space for such software components which previously may have used hidden sectors on MBR formatted disks. The UEFI specification does not allow hidden sectors on GPT-formatted disks. For example, the Logical Disk Manager (LDM), on dynamic disks, stores metadata in a 1 MB area at the end of the disk which is not allocated to any partition. Formerly, on disks formatted using the master boot record (MBR) partition layout, certain software components used hidden sectors of the disk for data storage purposes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
